Introduction to FRP Tanks
Understanding FRP Tanks
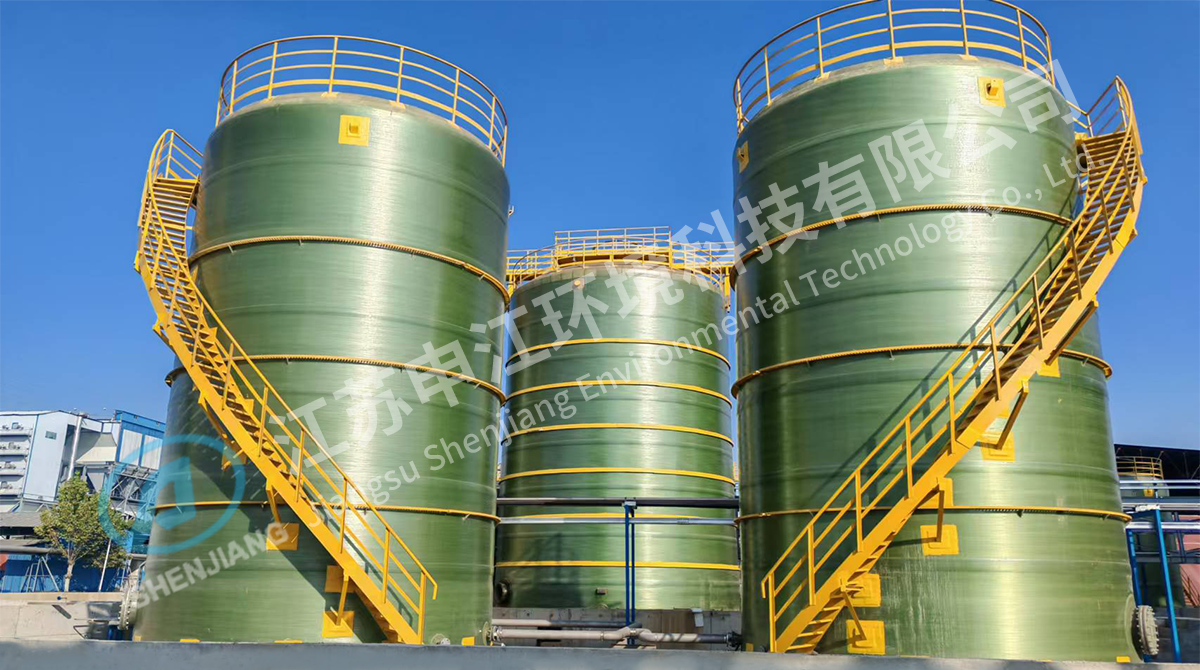
Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP), also known as composite material, is composed of fine glass fibers embedded in a resin matrix. This combination creates a material that is both lightweight and strong, with a high degree of corrosion resistance. FRP tanks, or fiberglass tanks, are designed using this material to provide storage solutions for a variety of liquids, including chemicals, water, and other industrial fluids. Compared to traditional steel or concrete tanks, FRP tanks offer unique properties that make them suitable for industrial applications, water treatment facilities, and chemical storage systems.
Composition and Properties of FRP
The structure of an FRP tank involves layers of fiberglass reinforced plastic, which include glass fibers and polymer resins such as polyester, vinyl ester, or epoxy. These layers are combined through processes like filament winding, hand lay-up, or spray-up techniques to form a durable tank wall. The glass fibers provide tensile strength, while the resin binds the fibers together and protects them from chemical attack and environmental degradation. FRP properties include resistance to corrosion, lightweight construction, flexibility in design, and ease of maintenance, which makes FRP tanks suitable for both chemical storage tanks and water storage tanks in various industrial settings.
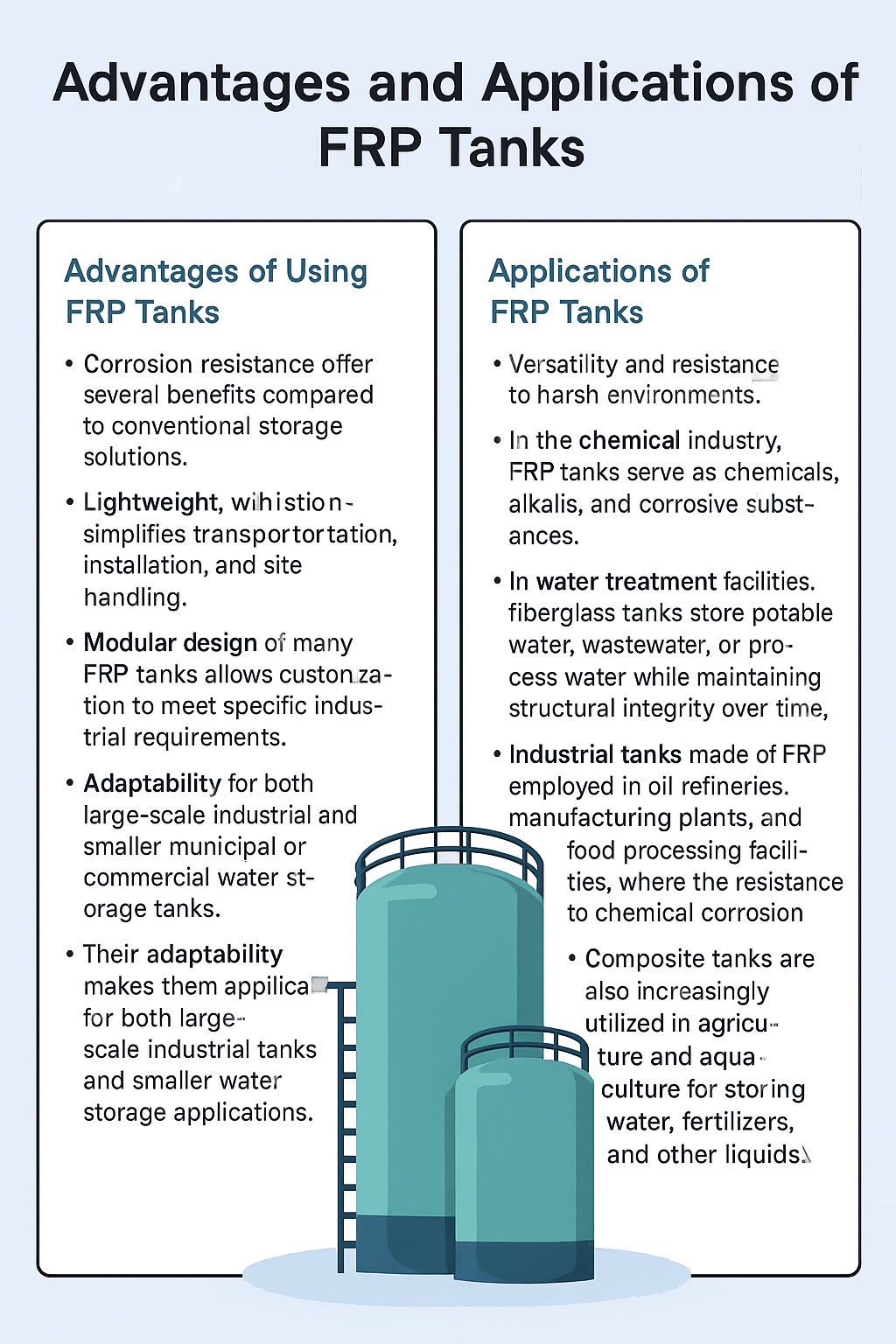
Advantages of Using FRP Tanks
FRP tanks offer several benefits compared to conventional storage solutions. Their corrosion resistant nature ensures longevity even when storing aggressive chemicals or saltwater. They are lightweight, which simplifies transportation, installation, and site handling. The modular design of many FRP tanks allows customization to meet specific industrial requirements. Additionally, FRP tanks have smooth internal surfaces, reducing the risk of contamination in chemical or water storage applications. Their adaptability makes them applicable for both large-scale industrial tanks and smaller water storage tanks in municipal or commercial projects.
Applications of FRP Tanks
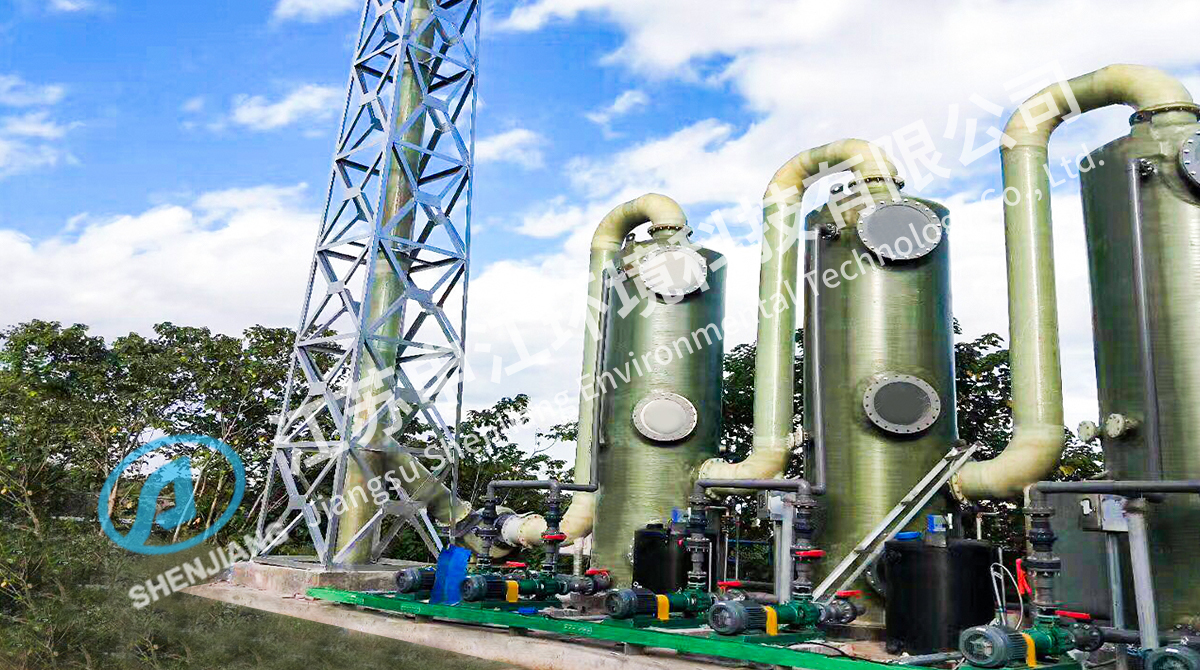
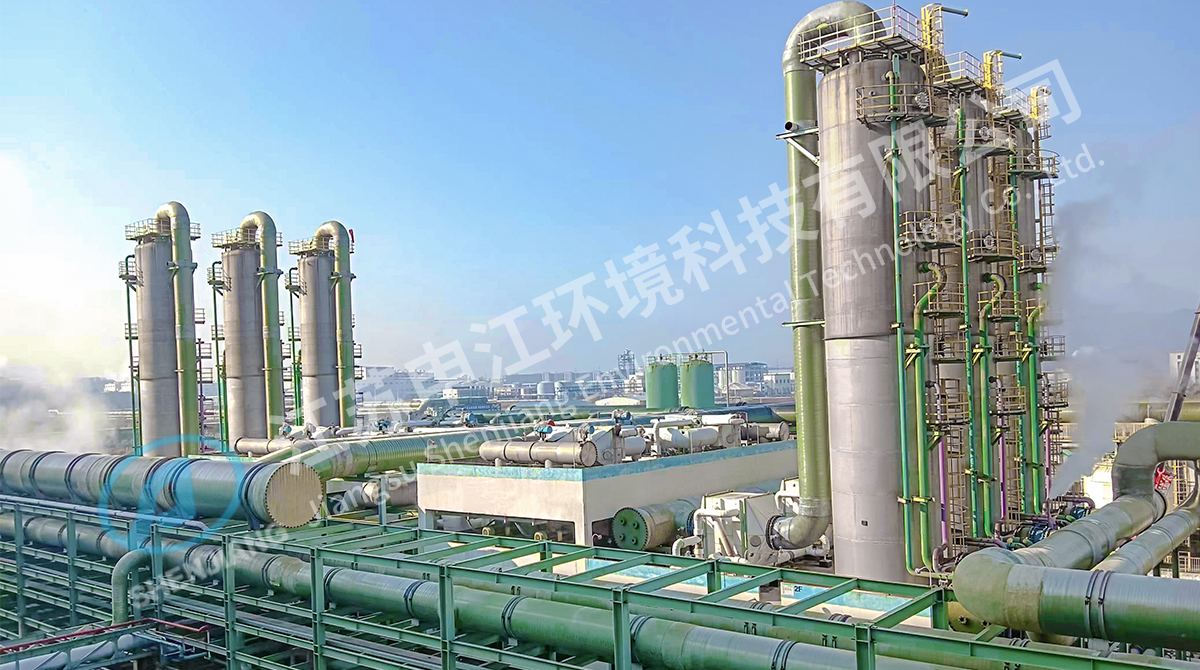
FRP tanks are widely used across industries due to their versatility and resistance to harsh environments. In the chemical industry, FRP tanks serve as chemical storage tanks for acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances. In water treatment facilities, fiberglass tanks store potable water, wastewater, or process water while maintaining structural integrity over time. Industrial tanks made of FRP are employed in oil refineries, manufacturing plants, and food processing facilities, where the resistance to chemical corrosion is crucial. Composite tanks are also increasingly utilized in agriculture and aquaculture for storing water, fertilizers, and other liquids.
Types of FRP Tanks
FRP tanks are available in various designs to meet different storage needs. Vertical cylindrical tanks are common for chemical storage, providing efficient use of floor space. Horizontal tanks are often used for water storage, allowing easier transportation and placement in confined areas. Custom-shaped FRP tanks are designed for specific industrial processes, enabling integration into existing piping or equipment setups. In addition, modular FRP tanks can be assembled onsite, which is beneficial for large-scale applications where transportation of pre-assembled tanks would be challenging.
Design Considerations for FRP Tanks
When designing an FRP tank, several factors need consideration, including the chemical compatibility of the resin, the expected temperature range, and the structural load. Engineers must ensure that the tank wall thickness and reinforcement layers are sufficient to withstand internal pressures and environmental stresses. For chemical storage tanks, the resin type is chosen based on its resistance to the stored chemicals. For water storage tanks, UV-resistant resins may be used to prevent degradation from sunlight exposure. Proper design ensures the tank’s durability, safety, and performance over its operational life.
Installation and Maintenance of FRP Tanks
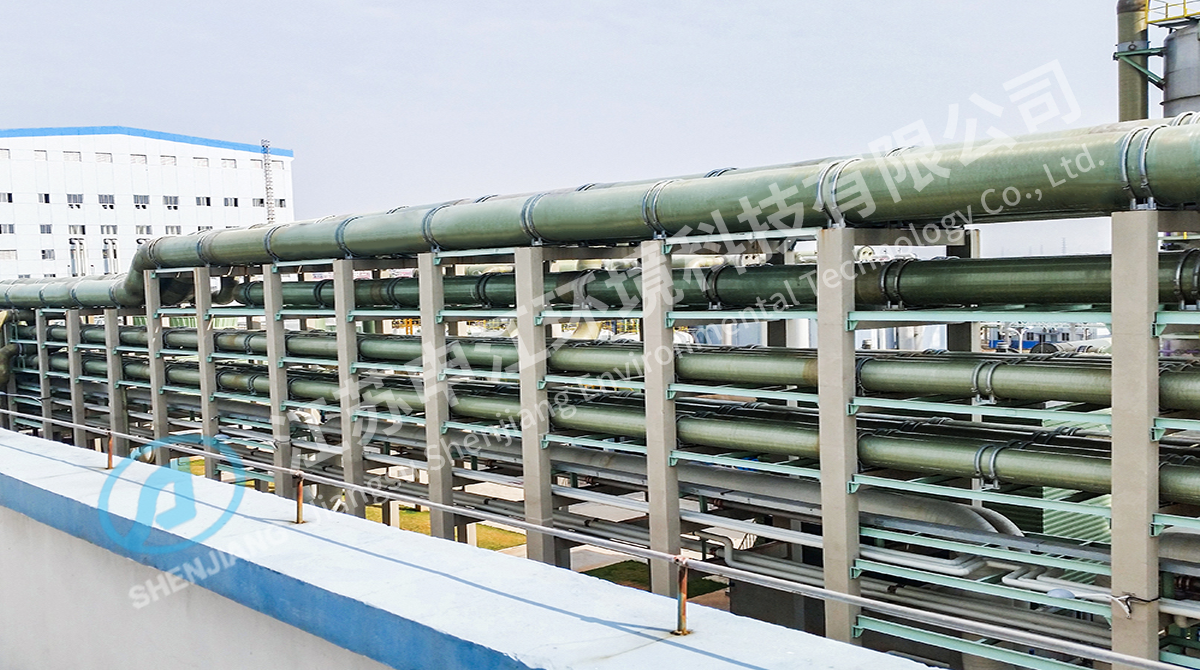
The installation of FRP tanks requires careful handling due to their large size and lightweight structure. Tanks should be placed on stable, level foundations, and fittings such as inlets, outlets, and overflow connections should be properly sealed to prevent leaks. Maintenance of FRP tanks is generally straightforward, as their corrosion resistant properties reduce the need for frequent repairs. Periodic inspection of the tank wall, fittings, and support structures helps ensure the tank remains in good condition. Cleaning should be done using non-abrasive methods to avoid damaging the resin surface while maintaining hygiene for water or chemical storage applications.
Comparison of FRP Tanks with Traditional Tanks
|
Tank Type
|
Material
|
Corrosion Resistance
|
Weight
|
Maintenance
|
Typical Applications
|
|
FRP Tank
|
Fiberglass reinforced plastic
|
High
|
Lightweight
|
Low
|
Chemical storage, water storage, industrial tanks
|
|
Steel Tank
|
Carbon steel / Stainless steel
|
Moderate
|
Heavy
|
Moderate to High
|
Industrial storage, water storage
|
|
Concrete Tank
|
Reinforced concrete
|
Low to Moderate
|
Very Heavy
|
High
|
Water storage, wastewater storage
|
Environmental and Safety Considerations
FRP tanks provide environmental advantages due to their resistance to chemical leakage and contamination. The corrosion resistant tank design reduces the likelihood of spills, protecting the surrounding environment. In addition, FRP materials are non-reactive with many stored chemicals, enhancing safety for personnel handling the tanks. Unlike metal tanks, FRP tanks do not require protective coatings that may involve hazardous substances, making them a safer choice for industrial and municipal applications.
Future Trends in FRP Tank Applications
With advancements in composite materials, FRP tanks are expected to see increasing use in specialized applications. Innovations in resin technology are improving chemical resistance and UV stability, expanding the potential for outdoor installations and aggressive chemical storage. The modular design of composite tanks allows for more flexible installation in complex industrial setups. FRP maintenance continues to be simplified through surface treatments and design improvements, making these tanks an increasingly practical solution for chemical, water, and industrial storage needs.
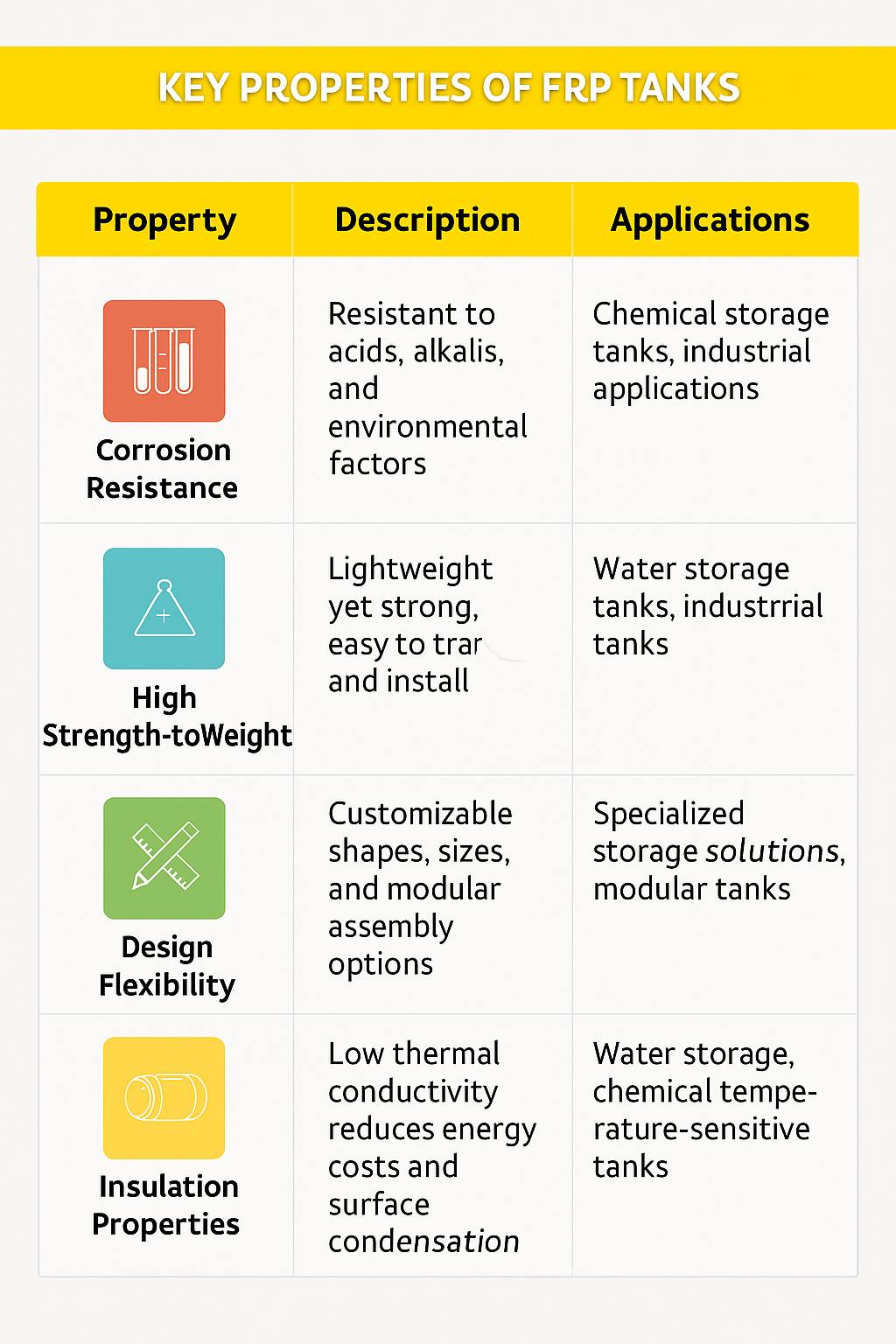
Key Properties of FRP Tanks
Corrosion Resistance of FRP Tanks
FRP tanks, constructed from fiberglass reinforced plastic, exhibit a high level of corrosion resistance, which is one of the primary reasons for their widespread use in industrial and chemical storage applications. The resin matrix in FRP acts as a barrier against chemical attack, preventing acids, alkalis, and other reactive substances from compromising the structural integrity of the tank. Unlike metal tanks, which are prone to rust and deterioration when exposed to moisture or corrosive chemicals, FRP tanks maintain their integrity over extended periods of use. This corrosion resistant tank property ensures that the stored liquids, whether water or chemical solutions, remain uncontaminated and that the tank structure remains stable under harsh environmental conditions. Additionally, the resistance to UV rays and environmental weathering makes FRP tanks suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
One of the key FRP properties is its high strength-to-weight ratio. Despite being lightweight, FRP tanks provide substantial structural strength, allowing them to hold large volumes of liquids without compromising safety or stability. This lightweight nature simplifies handling, transportation, and installation, especially in areas where moving heavy steel or concrete tanks would be challenging. For industrial applications, the reduced weight of composite tanks decreases the load on supporting structures and foundations, enabling more flexible design solutions. Moreover, the high strength-to-weight ratio of fiberglass tanks contributes to their durability and resilience under varying pressure and environmental conditions, making them suitable for chemical storage tanks, water storage tanks, and other industrial storage solutions.
Design Flexibility of FRP Tanks
FRP tanks offer significant design flexibility compared to traditional storage solutions. Engineers and designers can customize the shape, size, and wall thickness of composite tanks to meet specific operational requirements. Vertical, horizontal, and custom-shaped FRP tanks can be produced to fit confined spaces or complex industrial setups. Modular FRP tanks allow for onsite assembly, providing additional flexibility for large-scale installations. The ability to integrate inlet and outlet connections, inspection ports, and other accessories during the design phase enhances the usability of FRP tanks in water treatment plants, chemical storage facilities, and industrial environments. Design flexibility ensures that FRP tanks can meet both standard and specialized storage needs efficiently.
Insulation Properties of FRP Tanks
Fiberglass reinforced plastic possesses natural insulation properties, which can help in reducing energy costs in certain applications. FRP tanks exhibit low thermal conductivity, which limits the transfer of heat or cold between the stored liquid and the external environment. This is particularly advantageous for water storage tanks, where temperature control may be important, or for chemical storage tanks where temperature fluctuations can affect chemical stability. The insulation provided by FRP tanks minimizes the need for additional heating or cooling systems, contributing to operational efficiency and overall cost savings. The inherent insulation properties also improve safety by reducing surface condensation and maintaining consistent internal temperatures in various industrial applications.
Long Service Life of FRP Tanks
FRP tanks are recognized for their long service life, which results from the combination of corrosion resistance, high structural strength, and resistance to environmental degradation. With proper installation and regular maintenance, fiberglass tanks can remain functional for several decades. The durability of composite tanks reduces the need for frequent replacements, which is particularly beneficial in industrial and municipal water treatment settings. Long service life also contributes to sustainable operations, as fewer resources are required for manufacturing and installation over time. Periodic inspections, cleaning, and minor maintenance activities ensure that FRP tanks continue to perform effectively, maintaining both safety and efficiency for chemical and water storage applications.
Key Properties of FRP Tanks
|
Property
|
Description
|
Applications
|
|
Corrosion Resistance
|
Resistant to acids, alkalis, and environmental factors
|
Chemical storage tanks, industrial applications
|
|
High Strength-to-Weight
|
Lightweight yet strong, easy to transport and install
|
Water storage tanks, industrial tanks
|
|
Design Flexibility
|
Customizable shapes, sizes, and modular assembly options
|
Specialized storage solutions, modular tanks
|
|
Insulation Properties
|
Low thermal conductivity reduces energy costs and surface condensation
|
Water storage, chemical temperature-sensitive tanks
|
|
Long Service Life
|
Durable material ensures extended operational life with minimal maintenance
|
Industrial storage, water treatment facilities
|
FRP Maintenance Considerations
While FRP tanks are durable, regular maintenance enhances their operational efficiency and lifespan. Inspection of the tank surface for any cracks, wear, or resin degradation is recommended periodically. Cleaning should be conducted with non-abrasive methods to prevent damage to the fiberglass reinforced plastic layers. Ensuring proper sealing of inlets, outlets, and inspection ports minimizes leakage risks and maintains chemical integrity. Routine maintenance also includes checking structural supports and fasteners to ensure the tank remains stable. These practices help preserve the properties of corrosion resistant tanks and support the long-term performance of FRP storage solutions.
Applications of FRP Tanks
The combination of corrosion resistance, strength, design flexibility, insulation, and long service life makes FRP tanks suitable for a variety of applications. In industrial environments, FRP tanks store chemical solutions, wastewater, and process liquids safely. Municipal and commercial water treatment facilities use fiberglass tanks for potable water, wastewater, and storage of process water. Composite tanks are also applied in agriculture for water storage, fertilizer solutions, and irrigation systems. In addition, the lightweight nature of FRP tanks allows them to be deployed in remote or temporary installations where traditional steel or concrete tanks would be impractical.
Environmental and Safety Advantages
FRP tanks contribute to environmental protection and operational safety. Their resistance to chemical leakage and contamination reduces the risk of environmental damage in case of spills. The non-reactive nature of fiberglass reinforced plastic ensures that chemicals are stored safely without interacting with the tank walls. Additionally, the insulation properties of FRP tanks can improve safety by maintaining stable temperatures and preventing condensation. Compared to metal tanks, FRP tanks do not require protective coatings that may contain hazardous substances, making them safer for workers and the surrounding environment.
Future Outlook for FRP Tanks
The future of FRP tanks involves continuous improvements in composite materials, resin formulations, and design methodologies. Advancements in UV-resistant and chemically stable resins will allow FRP tanks to be used in more demanding outdoor and industrial applications. Modular and custom-designed composite tanks will further enhance their adaptability to complex storage requirements. Simplified maintenance procedures and extended service life will continue to make FRP tanks a practical choice for chemical storage, water storage, and various industrial applications. As industries increasingly seek corrosion resistant, lightweight, and flexible storage solutions, FRP tanks are expected to maintain their relevance in modern storage systems.
Advantages of Using FRP Tanks
Cost-Effectiveness of FRP Tanks
FRP tanks, constructed from fiberglass reinforced plastic, present notable cost advantages over traditional steel or concrete tanks when analyzed over their full lifecycle. While the initial purchase price of FRP tanks may be comparable to other materials, the total lifecycle cost is generally lower due to reduced maintenance, longer service life, and resistance to corrosion. Steel tanks, for example, often require periodic painting or coating to prevent rust, while concrete tanks may experience cracking or leakage over time, necessitating repairs. In contrast, corrosion resistant tanks made of FRP maintain structural integrity over decades, reducing the frequency and expense of repairs or replacements. This cost-effectiveness makes FRP tanks an attractive option for chemical storage tanks, water storage tanks, and industrial tanks, particularly for facilities that aim to optimize long-term operational budgets without compromising storage reliability.
Reduced Maintenance Requirements
One of the primary advantages of fiberglass tanks is their low maintenance needs. The non-reactive nature of fiberglass reinforced plastic ensures that FRP tanks resist degradation caused by chemicals, moisture, and environmental conditions. Unlike metal tanks that may require rust treatment or replacement of corroded components, FRP tanks can be cleaned with standard non-abrasive methods and inspected periodically without extensive maintenance efforts. The resin and reinforcement materials in composite tanks provide long-term durability, reducing the frequency of maintenance interventions. Proper FRP maintenance typically includes visual inspections for surface wear, checking seals and connections, and cleaning internal surfaces. This reduced maintenance requirement is particularly beneficial in industrial applications, chemical storage, and water treatment facilities, where minimizing downtime and labor costs is crucial.
Ease of Installation
FRP tanks are designed for straightforward installation, which is facilitated by their lightweight and modular construction. Compared to heavy steel or concrete tanks, composite tanks can be transported and assembled more easily, even in areas with limited access or restricted space. Modular FRP tanks allow for onsite assembly, reducing logistical challenges and installation time. The ability to customize tank dimensions and include integrated inlets, outlets, and inspection ports during manufacturing further simplifies the installation process. For industrial applications and water storage projects, the ease of installation translates to faster deployment and reduced labor costs. Additionally, the lightweight nature of FRP tanks reduces the need for extensive foundation reinforcement, making them suitable for both permanent and temporary storage solutions.
Environmental Benefits of FRP Tanks
Fiberglass reinforced plastic tanks provide environmental advantages due to their long lifespan, durability, and energy efficiency. The extended service life of FRP tanks minimizes the frequency of replacement, reducing the environmental impact associated with manufacturing, transporting, and disposing of tanks. Additionally, the insulation properties of FRP tanks reduce energy consumption for temperature-sensitive storage applications, further contributing to eco-friendly operations. Unlike some metal tanks that require coatings containing volatile organic compounds, FRP tanks are constructed from materials that do not emit harmful chemicals during regular use. These environmental benefits make FRP tanks suitable for sustainable water storage, chemical storage, and industrial applications, supporting operational practices that consider both efficiency and ecological impact.
Advantages of FRP Tanks
|
Advantage
|
Description
|
Application Examples
|
|
Cost-Effectiveness
|
Lower lifecycle costs due to minimal repairs and long service life
|
Industrial tanks, water storage tanks
|
|
Reduced Maintenance
|
Minimal upkeep required thanks to corrosion resistance and durable composite materials
|
Chemical storage tanks, municipal water tanks
|
|
Ease of Installation
|
Lightweight and modular design allows fast deployment and reduced labor
|
Modular water storage, chemical plants
|
|
Environmental Benefits
|
Long lifespan and low energy use reduce ecological impact
|
Water treatment, industrial storage
|
FRP Tanks in Industrial Applications
FRP tanks are widely used across various industrial sectors due to their combination of cost-effectiveness, durability, and ease of maintenance. In chemical processing plants, FRP tanks serve as corrosion resistant tanks for storing acids, alkalis, and other reactive substances. Their design flexibility allows the integration of multiple connections, valves, and instrumentation to support complex chemical processes. In the water treatment sector, fiberglass tanks provide reliable water storage solutions for potable water, wastewater, and process water, while minimizing maintenance costs and operational interruptions. Industrial tanks made of composite materials also find applications in agriculture, food processing, and energy sectors, where safe and durable storage is essential. The versatility of FRP tanks allows them to adapt to a wide range of storage needs while maintaining cost and operational efficiency.
Comparative Lifecycle Analysis
When comparing FRP tanks with steel and concrete alternatives, several factors highlight the long-term advantages of fiberglass reinforced plastic. Steel tanks require periodic surface treatments and are prone to rust, which increases maintenance costs over time. Concrete tanks can develop cracks, leading to leakage and structural repair needs. FRP tanks, by contrast, resist corrosion, maintain structural strength, and require minimal maintenance, reducing total lifecycle costs. The lightweight nature of FRP tanks also contributes to reduced transportation and installation expenses. Additionally, the durability and design flexibility of composite tanks ensure that operational efficiency is maintained over extended periods, further supporting their cost-effectiveness in large-scale industrial and municipal projects.
Safety Considerations
The use of FRP tanks contributes to operational safety due to their chemical resistance, structural integrity, and thermal insulation properties. Corrosion resistant tanks prevent leakage or contamination of stored liquids, reducing environmental and safety risks. The natural insulation of fiberglass reinforced plastic helps maintain stable internal temperatures, which is critical for chemical storage where temperature fluctuations could lead to hazardous reactions. Additionally, FRP tanks do not produce sparks or react with most stored chemicals, making them suitable for storage of flammable or reactive substances in industrial settings. These safety benefits, combined with the advantages of reduced maintenance and cost-effectiveness, make FRP tanks a preferred choice in various industrial and municipal applications.
FRP Tank Maintenance Practices
Although FRP tanks require less maintenance than traditional storage solutions, regular care ensures optimal performance and extended service life. Routine maintenance includes inspecting the tank surface for cracks, checking seals and fittings, cleaning internal surfaces to prevent contamination, and monitoring structural supports. Non-abrasive cleaning methods preserve the integrity of the fiberglass reinforced plastic layers. Proper maintenance of composite tanks not only ensures the safe storage of water, chemicals, or industrial liquids but also supports operational efficiency and sustainability. Facilities that adhere to consistent FRP maintenance schedules benefit from fewer unexpected repairs and longer-lasting storage solutions.




 English
English  中文简体
中文简体 Español
Español عربى
عربى русский
русский ไทย
ไทย Indonesia
Indonesia Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
















